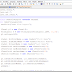
A simple Java method requires a minimum of three items:
Visibility : public, private, protected
Return Type: void, int, double, (etc.)
name: whatever you want to call the method
Return Type: void, int, double, (etc.)
name: whatever you want to call the method
Visibility means who can access it. If it is public, anyone who
has access to your class file can access the method. In some
circumstances, this is perfectly fine. If the method is private, only
the functions inside of that class can call the method. This is used as
utility methods to do something you do not want just anyone who uses the
class to do. Protected gives public function to all child classes.
Return type is void if you do not want the method to give you any
data back. It would be used for such things as a method that prints out
something. Any other return requires a return statement with the type
of data it returns. For example, if you add two integers and want the
results of that integer, your return type would be int.
Name of the method is anything you choose that is not already
used in the class (unless you are overloading the method which is beyond
the scope of this article)
If you want the method to do something with the data you supply it, you also need to include parameters
within the ( ) You include what data type it is and give that parameter
a name (ie: you are declaring a local variable for that method only)
How to invoke (call) a method (method invocation):
When a method is
invoked (called), a request is made to perform some action, such as
setting a value, printing statements, returning an answer, etc.
The code to invoke the method contains the name of the method to be
executed and any needed data that the receiving method requires.
The required data for a method are specified in the method's parameter
list.
example :
int temp = thisIsMethod("Koko", 17);
or
System.out.println(thisIsMethod("Koko", 17));







0 comments
Post a Comment